CVE-2024–38063
WINDOWS TCP/IP RCE VULNERABILITY

DESCRIPTION
CVE-2024-38063 is a highly critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability found in the Windows TCP/IP stack, particularly when handling IPv6 traffic. This vulnerability has been assigned a severity score of 9.8 out of 10, highlighting the seriousness of this issue. Attackers can exploit this vulnerability by sending specially crafted IPv6 packets to the target system, enabling them to execute arbitrary code without the need for user interaction or authentication.
This vulnerability is particularly dangerous because it resides within the core network protocol (TCP/IP), which is fundamental to internet communications. Therefore, its potential impact could be very broad, especially if the exploitation spreads. While there is currently no evidence that this vulnerability has been actively exploited, Microsoft has categorized this exploit as "more likely" to occur, making it a high priority for immediate remediation.
Vector: CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H
AFFECTED SYSTEMS
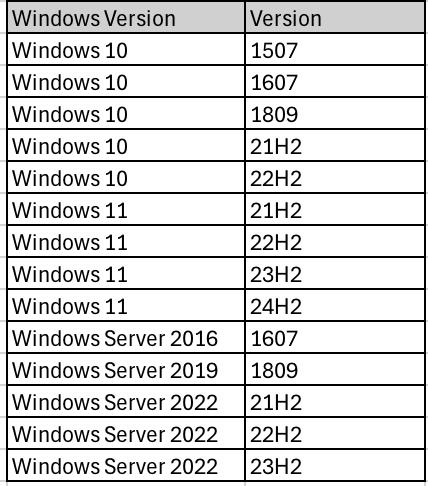
Affected Versions CVE-2024–38063
The systems impacted by the vulnerability CVE-2024-38063 include various versions of Windows that utilize the TCP/IP stack with IPv6 enabled. Here is a list of vulnerable Windows versions:
VULNERABILITY IMPACT
CVE-2024-38063 has several serious impacts that can affect vulnerable systems, especially in the context of remote code execution (RCE) without user interaction. Here are some of the major impacts of this vulnerability:
Arbitrary Code Execution: Attackers can execute arbitrary code on the target system simply by sending specially crafted IPv6 packets. This can give attackers full control over the affected system, including installing malicious software, stealing data, or altering system configurations.
User Interaction Not Required (0-Click Vulnerability): One of the most dangerous aspects of CVE-2024-38063 is that the attack can be executed without requiring any interaction from the target user, making it highly exploitable and risky.
High Exploitability Likelihood: Although there are no reports of active exploitation of this vulnerability yet, Microsoft has identified it as "more likely" to be exploited. This indicates that the risk of attacks exploiting this vulnerability is quite high if patches are not promptly applied.
RECOMMENDATIONS
To protect systems from this vulnerability, the following steps are recommended:
• Promptly Apply Security Patch: Implement the security patch released by Microsoft as soon as possible. This is the most direct and effective way to address the vulnerability and prevent potential exploits.
• Disable IPv6 as a Temporary Mitigation: If IPv6 is not needed, consider disabling it on systems as an interim measure until the patch can be applied. This can reduce the attack surface and mitigate the risk of this specific vulnerability.
The vulnerability impacts systems that utilize IPv6 as part of their network configurations. Systems that do not use IPv6 or have IPv6 disabled will not be affected by this vulnerability.